Effect Of Multiplying By Diagonal Matrix
All you have to compute are the diagonal elements. Is a diagonal matrix whose entries contain the variables that need to be optimized those variables can be assumed to be real without loss of generality.

2 1 Operations With Matrices 2 2 Properties Of Matrix Operations Ppt Video Online Download
Multiplying by D 1 0 0 1 one gets B D A 0 1 1 0.
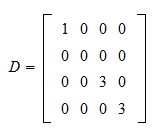
Effect of multiplying by diagonal matrix. In this case all the off diagonal elements are assigned zero. Where M is a mn dense rectangular matrix with no specific structure and D is a mm diagonal matrix with all positive elements. Effect of multiplying a matrix by a diagonal matrix.
The effect is that of multiplying the i-th row of matrix A by the where L is a diagonal matrix defined by setting the diagonal elements of L to the elements of the vector l. A diagonal matrix with all diagonal entries equal to 1. Left-multiplication be a diagonal matrix does not have any simple effect on eigenvalues and given that eigenvalues are perturbed or destroyed what could one possibly want to say about corresponding eigenvectors.
Where M is a mn dense rectangular matrix with no specific structure and D is a mm diagonal matrix with all positive elements. C ii a ii b ii and all other entries are 0. Diagonal matrices have some properties that can be usefully exploited.
The emitted spectrum for an object with reflectance vector r under illumination l is given by multiplying the reflectance by the illuminant at each wavelength g Lr. The identity matrix is diagonal. Example in R 2.
Multiplying two or more diagonal matrices produces a diagonal matrix. The effect is that of multiplying the i-th row of matrix A by the factor k i ie. I then discussed block diagonal matrices ie block matrices in which the off-diagonal submatrices are zero and in a multipart series of posts showed that we can uniquely and maximally partition any square matrix into block.
Therefore it is triangular and its determinant is equal to the product of its diagonal entries. Effect of multiplying a matrix by a scalar. Diagonal matrix general matrix matrix multiplication multiplication.
I wish to find the most efficient way to implement the following equation. The successive rows of the original matrix are simply multiplied by successive diagonal elements of the diagonal matrix. The product AB is defined to be the mp matrix C cij such that cij Pn k1 aikbkj for all indices ij.
In this particular example the diagonal entries of are so multiplying by stretches or dilates eachHHboth bigger than B coordinate. Finally consider multiplying two diagonal matrices. At first sight I thought it would be easy but Im finding myself stuck since any of the ideas I had in mind to do that have been.
An m-by-n matrix is a rectangular array of numbers that has m rows and n columns. In a previous post I discussed the general problem of multiplying block matrices ie matrices partitioned into multiple submatrices. This sub-section presents an easy-to-prove proposition about the multiplication of a matrix by a scalar.
The effect of the diagonal matrix on the same point when described in H B U-coordinates. Inverse of Symmetric Matrix Plus Diagonal Matrix if Square Matrixs Inverse Is Known 4 Multiplication of unitary matrices to make symmetric off-diagonal elements zero. What is the effect of post-multiplying a matrix.
Multiplication of diagonal matrices is commutative. What is the effect of pre-multiplying a matrix by a diagonal matrix A. I1 1 I2 1 0.
Matrix multiplication The product of matrices A and B is defined if the number of columns in A matches the number of rows in B. Let A aik be an mn matrix and B bkj be an np matrix. In other words matrix multiplication which is in general not commutative becomes commutative when all the matrices involved in the multiplication are diagonal.
The nn identity matrix is denoted In or simply I. If A and B are diagonal then C AB BA. In addition m n and M is constant throughout the course of the algorithm with only the elements of D changing.
This is pictured below for standard coordinates where. With A 0 1 1 0 one has eigenvalues 1 1 with eigenvectors that you can easily spot. To find the value of each of the diagonal.
Multiplying it by the diagonal matrix Q 8 ensures that the 2-norm of each basis vector v i of V 8 is equal to unity ie 555 v i 2 k 0 7 v i k 2 1 i k 0 1. If A and B are diagonal then C AB is diagonal. Before reading the proof try to prove it by yourself as an.
Further C can be computed more efficiently than naively doing a full matrix multiplication. Diagonal matrices as was explained earlier are square matrices. In addition m n.
Effect on eigenvalues of multiplying by a diagonal matrix. That is matrices are.

Sign In Or Register Studying Math Matrix Multiplication Teaching Math

Diagonal Matrix An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
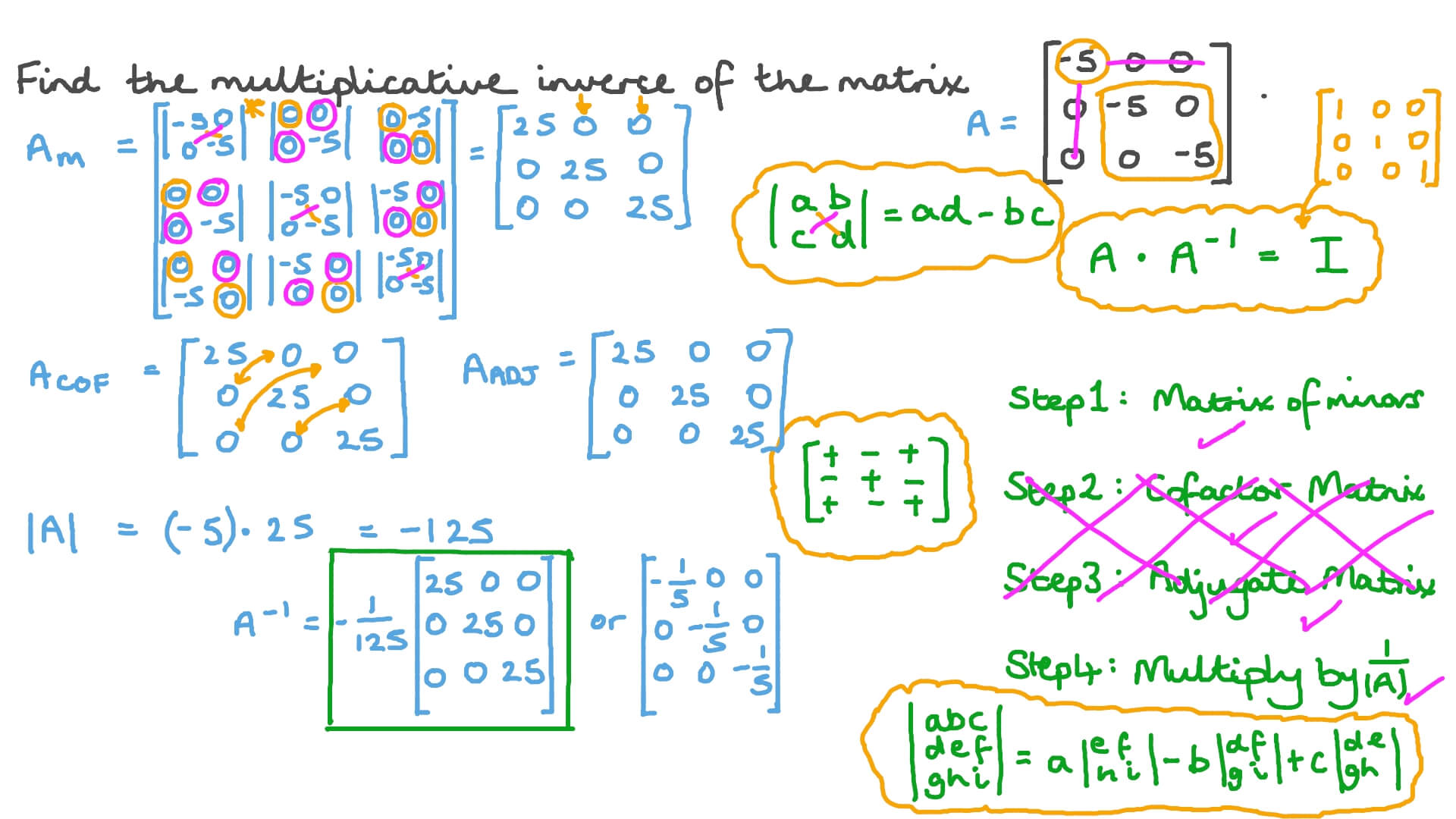
Question Video Finding The Inverse Of A Diagonal Matrix Nagwa
Effect Of Multiplying A Matrix By A Diagonal Matrix
For A Symmetric Matrix With Different Diagonal Elements Is There A Shortcut Method Other Than The Conventional One To Find Its Determinant Quora

Mathematics Medicine What Is Meant By A Matrix A Matrix Is A Set Of Numbers Arranged In The Form Of A Rectangle And Enclosed In Curved Brackets Ppt Download

Effect Of Multiplying A Matrix By A Diagonal Matrix
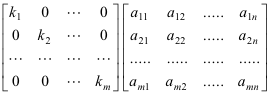
Effect Of Multiplying A Matrix By A Diagonal Matrix
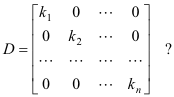
Effect Of Multiplying A Matrix By A Diagonal Matrix

Rules Of Matrix Arithmetic Ppt Video Online Download
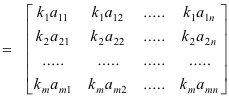
Effect Of Multiplying A Matrix By A Diagonal Matrix

Diagonal Matrix An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
A Geometrical Understanding Of Matrices

Chapter 2 Matrices 2 1 Operations With Matrices

2 1 Operations With Matrices 2 2 Properties Of Matrix Operations Ppt Video Online Download
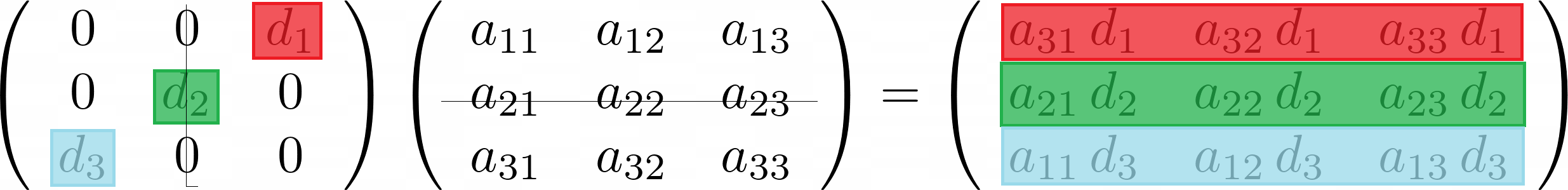
Visualizing Matrix Multiplication In Four Different Ways Part 2 By Vaibhav Patel Analytics Vidhya Medium

Mathematics Medicine What Is Meant By A Matrix A Matrix Is A Set Of Numbers Arranged In The Form Of A Rectangle And Enclosed In Curved Brackets Ppt Download
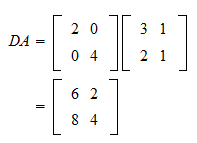
Multiplication By A Diagonal Matrix